Curriculum defined
Curriculum is a broad plan that is made by school and it includes educational experiences to achieve its aims, goals and objectives and students have these educational experiences under the guidance of the school. Therefore, Curriculum has ten basic patterns that are discussed below:
1. Child-Centered Curriculum
It is also called learner-centered curriculum. The philosophy underlying this curriculum is that the children is that the center of the educational process. This pattern of curriculum bases upon the abilities and the interest of the learners and students have experiences and diverse learning activities rather than rote learning. Learner-centered classrooms focus primarily on individual students’ learning. The teacher’s role is to facilitate growth by utilizing the interests and unique needs of students as a guide for meaningful instruction.
This curriculum allows the students to actively participate in discovery learning processes and a variety of hands-on activities are administered in order to promote successful learning. And it focuses upon a child as a learner being a center of activities in a learning center.
2. Teacher-Centered Curriculum
In this curriculum, the focus is upon teacher’s teaching skills and the way of delivery of the content. It emphasizes the importance of transmitting of knowledge, skills and information from a teacher to students. A teacher is a center of knowledge and instills the respect of authority and makes children aware of their responsibilities. Teachers focus on making relationships with students that are anchored in intellectual explorations of selected materials.
They focus more on content than on student processing and this pattern of curriculum places more of the responsibility on delivering content rather than considering students needs and desires. The teacher plans each and everything about what to do in the class and students follow the teacher.
3. Core Curriculum
This type of curriculum is a set of common courses and is a general education for all students and common learning includes knowledge, skills and values and all learners are provided these learning experiences and these common learning experiences are expected essential for the learners to adjust effectively in the society and these learning sets the basic subjects like English, Math, History, Science etc.
This type of curriculum emphasizes on the total growth the of the pupil such as social, emotional, moral, intellectual, physical and spiritual and each learning experience aims at the total growth.
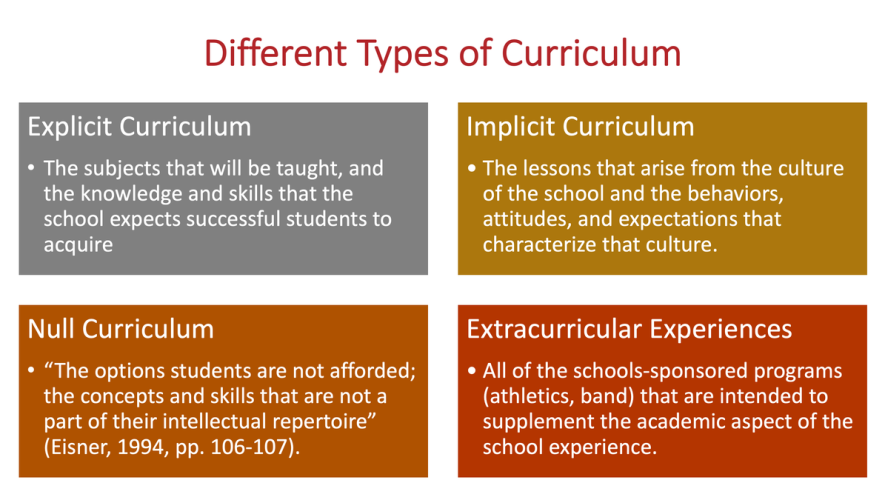
4.Overt, Explicit, or Written Curriculum
Written curriculum is simply that which is written as part of formal instruction of schooling experiences. It may refer to a curriculum document, texts, films, and supportive teaching materials that are overtly chosen to support the intentional instructional agenda of a school. Thus, the overt curriculum is usually confined to those written understandings and directions formally designated and reviewed by administrators, curriculum directors and teachers, often collectively.
5. Covert or Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum refers to the types of curriculum which is unplanned or unintended curriculum but plays a vital role in learning. It consists of norms, values, and procedures. The hidden curriculum refers to the way in which cultural values and attitudes (such as obedience to authority, punctuality, and delayed gratification) are transmitted, through the structure of teaching and the organization of schools
6. Integrated Curriculum
An integrated curriculum implies learning that is synthesized across traditional subject areas and learning experiences that are designed to be mutually reinforcing. This approach develops the child’s ability to transfer their learning to other settings. It is a unification of different subjects having interrelating themes and concepts. Teacher teaches various subjects by using integration techniques. For example, General Science curriculum integrates concepts from Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geology and Astronomy etc.
7. Subject-Centered Curriculum
These types of curriculum give importance to training pupils in particular subjects. Its main objectives are all the elements of knowledge that constitute a subject for study. Thus, the curriculum goes into the depth of the subject that gives specialized knowledge to the learner. The specialist teacher is appointed to deal with the subject in its analytical detail.
Higher education is characterized by this subject-centered curriculum. It leads to higher study, research, and experimentation of individuals on the subject. This type of curriculum is more appropriate for students of academic interest and creativity talents.
8. Broad Field or Holistic Curriculum
Broad field curriculum is a modification of subject centered curriculum. A broad field curriculum is a structure for achieving educational outcomes that combines related subjects into one broad field of study.
The purpose of a broad field curriculum is to highlight relationships between subjects and to integrate the learning experience. The broad field design combines two or more related subjects into a single broad field of study, for example, Language Arts combines the separate but related subjects of Reading, Spelling, Writing, Speaking, Listening, and Composition.
9. Activity Centered Curriculum
The type of curriculum that gives priority to active learning of a subject may be known as an activity curriculum. The verbal system of education neither suits the mental need of the child nor the circumstances of life. It is the philosophy of Pragmatism behind this curriculum which beliefs in learning to be practical, useful, and work-oriented. Activity involvement in learning naturally gives better results. Work is a natural and easier means of learning anything. It is also the native and natural tendency of children.
Further, the experience derived from work is more durable and more meaningful for life. So, modern educators like Froebel, Montessori, Dewey, and Gagne in their respective learning methods have designed this activity curriculum for children.
10. Null Curriculum
Eisner (1985) defined null curriculum as information that schools do not teach. Sometimes the teacher ignores some content or skill, deliberately or unknowingly. A teacher may consider some idea unimportant and ignore it. Similarly, teacher may avoid detailed description of some topic for the one or other reason. An example is the exclusion of Darwin’s theory of evolution from the official biology curriculum.
Cite This Article As:
Gulzar, A. A. (2021, March 27). Different Types of Curriculum. Retrieved from EDUCARE: https://educarepk.com/different-types-of-curriculum.html
OTHER RELATED POSTS

Dear Sir/Madam:
I believe your site is informative and educational which I have not referred for a long time. I took course like Instructional Media, Curriculum Inquiry, Teaching Methodology and Development Psychology long time ago – 1984/85. After three decades and half things have changed tremendously and I thought I am very far behind compared the innovation occurred to the education system. Therefore, I would like to know more on the Curriculum Development front through your site.
Regards,
Salahadin OMAR-AMIR
This site is among the most efficient and effective site I’ve ever use.thanks
thanks so much for information on curriculum.
i would like to know more about elements, models and types of Technical Vocational Education and training (TVET) specially in Uganda
I really appreciate you.
All the informations here are well ok.
HOW DO I CITE THIS GOOD ARTICLE