Introduction
Like any other business, organization or field of life, Education is also facing many challenges in this rapid changing era. To cope with the challenges, development in the field of education is a must, which can be brought best through research. Research and Development activities can help to evolve existing curricula, learning materials, teaching methodologies and techniques, and current assessment systems. So, research through development leads to innovation.
Definitions
Research and development (R&D) is the creation of new body of knowledge about existing products or processes, or the creation of an entirely new product. This is systematic creative work, and the resulting new knowledge is then used to formulate new materials or entire new products as well as to alter and improve existing ones.
Research and development (R&D) is a general term for all those investigative activities that an educational institute conducts with the intention of making a discovery that can either lead to the development of new educational products (e.g. curricula, learning materials) or procedures (e.g. teaching or assessment procedures), or to improvement of existing educational products or procedures.
Forms of Research and development (R&D)
Research and development is a key element for the success of any educational institute. R & D involves two major types of research by purpose. It combines systematically both basic and applied research, and aims at discovering solutions to problems or creating new educational products. It involves researching the market and the learners’ needs and developing new and improved products and services to fit these needs. It may take following forms:
Basic Research
When research aims to understand a subject matter more completely and build on the body of knowledge relating to it, then it falls in the basic research category. This research does not have much practical application. The findings of such research may often be of potential interest to a university.
Applied Research
Applied research has more specific and directed objectives. This type of research aims to determine methods to address a specific needs or requirements of learners/society. These investigations are all focused on specific objectives regarding products or processes e.g. determining methods to increase motivation of learners.
Development
Development is when findings of a research are utilized for the production of specific products including materials, systems and methods. Design and development of prototypes and processes are also part of this area. Development is research that generates requisite knowledge and designs for production and converts these into prototypes e.g. developing course materials or developing computer software for self-paced learning.
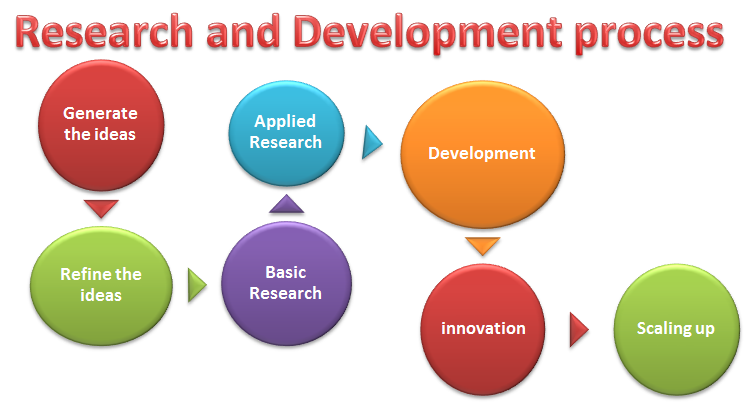
General R&D Process
The R&D may take months or years to yield useful products. Universities utilize this process for new product development and innovation. Though each college or university may have its own unique research methodology, a general research process will form the framework for it.
- Generate the ideas
- Research the market
- Identify learners’ needs
- Refine the ideas
- Focus ideas
- Identify the objectives
- Basic Research
- Hypothesize and clarify
- Synthesize and theorize
- Applied Research
- Concept testing research
- Design and test the product
- Development
- Develop and test prototype
- Innovation
- Development and marketing of technical invention
- Scaling up
- Commercialization of the product
R&D cell in Universities
Research and development (R&D) is a valuable tool for growing and improving universities. Almost all the universities have R&D Cell for this purpose. R&D depends on the size of university. In small universities, R&D tends to focus more on product improvement because of budget and cost limitations. Larger universities may be able to dedicate more time and resources to R&D to introduce new products as well as improve existing ones. The benefits of R&D are often long-term, so it’s important to remember that investment in it may not result in short-term profits. R&D can help to develop more efficient processes and new ways of delivering services as well as product development and improvement. Universities that have an R&D Cell have a greater chance of success than universities that don’t.
OTHER RELATED POSTS



The above mentioned details are worth understanding.
I need a complete structure of R&D Department in a franchise schooling system.
Can I get a document or any link?
I think say thank you very much this information. The steps of R and D very clear and systematically. But I will quest, how difference with DDR steps? thank you.
You are so interesting! I do not suppose I’ve truly read through something like this before. So good to discover another person with genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This site is one thing that’s needed on the web, someone with a bit of originality!