John Biggs and Kevin Collins (1982) developed the SOLO (Structure of Observed Learning Outcomes) taxonomy as a systematic way of describing how a learner’s performance grows in complexity when learning different subjects or mastering tasks. SOLO Taxonomy provides a simple, reliable and robust model for three levels of understanding i.e. Surface level, Deep level and Conceptual level (Biggs and Collis 1982).
Five Hierarchical Levels of Understanding
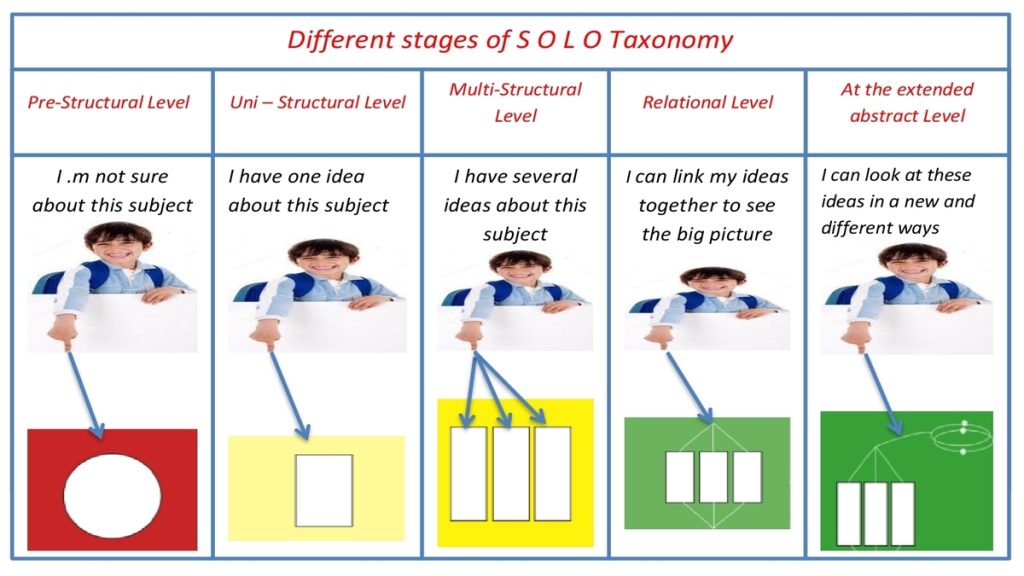
The SOLO taxonomy is divided into five performance levels of understanding. Performance levels of learners range from the lower end (Pre-structural) to the higher end (Extended Abstract). The SOLO taxonomy is hierarchical and each stage involves the previous and adds something to it.
SOLO 1: Pre-Structural Level
The learner is simply acquiring bits of unconnected information. He does not have any kind of understanding, uses irrelevant information and/or misses the point altogether.
Key Words (Verbs) — Learner misses the point, Fails, Remains unsuccessful, Flunks.
Example (Observable Behavior) — To a question like ‘What do you understand by the term respiration’ The learner responds;
“Err…..What?” or “I don’t know.”
SOLO 2: Uni-Structural Level
The learner can deal with one single relevant aspect of the subject or task. He is able to make simple and obvious connections, but the broader significance of the information is not understood.
Key Words (Verbs) — Define, Identify, Name, Draw, Find, Label, Match, Follow a simple procedure.
Example (Observable Behavior) — To a question like ‘What do you understand by the term respiration’ The learner responds;
“It releases energy.”
SOLO 3: Multi-Structural Level
The learner can understand several aspects of the subject or task, but its relationship to each other and to the whole remains separated. Ideas and concepts around a topic are not connected, rather they are treated independently.
Key Words (Verbs) — Describe, List, Outline, Complete, Continue, Combine, Calculate.
Example (Observable Behavior) — To a question like ‘What do you understand by the term respiration’ The learner responds;
“It is a chemical reaction that releases energy. It uses oxygen and glucose and releases carbon dioxide.”
SOLO 4: Relational Level
The student may understand relations between several aspects and how they might fit together to form a whole. The learner’s response demonstrates an understanding of the topic by being able to join all the parts together.
Key Words (Verbs) — Sequence, Classify, Compare and Contrast, Explain (cause and effect), Analyze, Form an analogy, Organize, Distinguish, Question, Relate, Apply, Describe.
Example (Observable Behavior) — To a question like ‘What do you understand by the term respiration’ The learner responds;
“It’s a reaction that takes place in all body cells. Products of digestion, such as glucose, are transported to cells by the blood and reacted with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide – which is breathed out. Energy is released.”
SOLO 5: Extended Abstract Level
The learner can make connections not only within the given subject field, but also make connections beyond it. He is able to generalize structure beyond what was given, may perceive structure from many different perspectives, and transfer ideas to new areas. He/she may have the competence to generalize, hypothesize, criticize or theorize.
Key Words (Verbs) — Generalize, Predict, Evaluate, Reflect, Hypothesis, Theorize, Create, Prove, Justify, Argue, Compose, Prioritize, Design, Construct, Perform, Explain, Apply, Analyze.
Example (Observable Behavior) — To a question like ‘What do you understand by the term respiration’ The learner responds;
“It’s a reaction that takes place in all body cells. Products of digestion, such as glucose, are transported to cells by the blood and reacted with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide – which is breathed out via the lungs (using gas exchange and ventilation). As energy is released, respiration is an example of an exothermic reaction. The energy that is released can then be used by the body for growth of new cells, repair of tissues and keeping warm.”
Advantages and Disadvantages of SOLO Taxonomy
Advantages
Advantages of the SOLO taxonomy include:
- Educators can use the verbs from the taxonomy to create learning outcomes. Unlike Bloom’s taxonomy, the verbs in the SOLO taxonomy are all observable, making them ideal for assessments.
- It provides a framework for creating progressive curricula that gradually increase in difficulty level.
- It provides a framework for thinking about what you want your students to know and at what stage.
- It helps you think through what grade you will give a student by explicitly outlining how to identify depth of understanding.
Disadvantages
Disadvantages include:
- The SOLO taxonomy doesn’t take into account difficulty of topics themselves. Some topics (such as brain surgery!) require extreme difficulty to reach levels 3 or 4 of the taxonomy. Other topics may be easy to understand, manipulate and theorize at level 5 of the taxonomy (extended abstract level). So, even very difficult postgraduate level curricula may require lower-order verbs within their learning outcomes.
- The SOLO taxonomy assumes courses should contain learning outcomes and places high value on assessment. Some educators may believe that assessment and learning outcomes stifle creativity and student-led learning and are therefore inappropriate.
References
Biggs, J.B., & Collis, K.F. (1982). Evaluating the quality of learning: The SOLO taxonomy. New York: Academic Press.
Biggs, J. B., & Tang, C. (2011). Teaching for quality learning at university (4th ed.). Berkshire: Open University Press.
OTHER RELATED POSTS
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
SOLO Taxonomy versus Bloom’s Taxonomy